Interventional Neuroradiology
General Information About Interventional Neuroradiology
St. Paul Radiology Interventional Neuroradiology is the largest and most experienced team of its kind in Minnesota, as well as one of the leading practices nationally. Patients have great confidence in choosing our services, not only because of the extensive volume of procedures that we perform and our highly trained staff, but also because of our accessibility, ease of scheduling, and close guidance through and beyond treatment. We are a multidisciplinary group that works alongside neurosurgeons and neurologists at the various institutions that we provide care for. We believe that the collaboration of subspecialty trained experts with dedicated skill sets allows for developing the best possible management plan for patients. We are available 24/7 for any and all consultations and second opinions. Please use our convenient online form below and we will reach out to you for more information.
Interventional neuroradiology uses minimally invasive techniques to treat vascular problems of the brain and spine. These treatment strategies involve the use of catheters, a thin flexible tube, to treat the problem from inside the blood vessel, (endovascular). Aneurysms, acute stroke, carotid stenosis and a number of other vascular diseases of the brain and spine may be treatable using interventional neuroradiology techniques. We additionally perform many nonvascular pain treatments of the spine including vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty and epidural steroid injections.

Interventional Neuroradiology Services
Vertebroplasty & Kyphoplasty
This minimally invasive procedure stabilizes a spinal fracture. A needle is guided into the fractured vertebra under x-ray guidance through a small puncture in the patient’s skin, and specially formulated acrylic bone cement is injected to stabilize the bone.
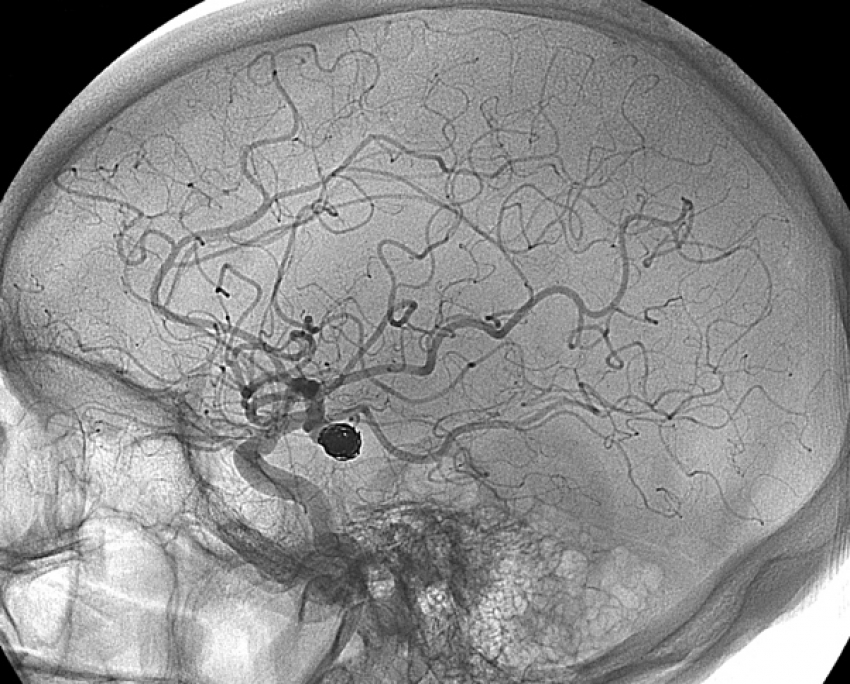
Diagnostic Angiograms
In this procedure, a catheter (a thin flexible tube) will be inserted into your leg or arm and the radiologist will flush a dye through the arteries to check blood flow and locate aneurysms, vascular malformations, blockages, narrowed vessels or other abnormalities.
Carotid Stenting
Carotid angioplasty and stenting is a minimally invasive procedure performed after a diagnostic angiogram to confirm the degree of vessel narrowing. During angioplasty, a balloon catheter is guided to the area of the blockage or narrowing. When the balloon is inflated, blood flow improves. A carotid stent (a small, metal mesh tube) is placed inside the carotid artery at the site of the blockage and provides support to keep the artery open.
Cerebral Aneurysm Coiling
This is a minimally invasive treatment for aneurysms that occur in the brain. A catheter is inserted through the skin into an artery and, using image-guidance, is maneuvered through the body to the aneurysm. Then, coils are inserted through the catheter and placed at the target site, to occlude the aneurysm. Blood clots around the coil(s), which helps block the flow of blood into the aneurysm and keep the vessel from rupturing or leaking.
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) and Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) Embolizations
This is a minimally invasive treatment for vessel malformations and fistulas that occur in the brain. A catheter is inserted through the skin into an artery and, using image-guidance, is maneuvered through the body to the target, where it is used to deliver a liquid similar to glue that clogs up the abnormal connection and restores normal circulation.
Tumor Embolizations
Tumor embolization is used to reduce or block the blood supply to a tumor by injecting a blocking agent (an embolic) through a catheter into a blood vessel. Blocking the blood supply to the tumor is intended to reduce blood loss during surgery.
Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Stroke
This procedure is the current gold standard for acute large vessel occlusions in the brain and involves mechanical removal of a blood clot. This is accomplished by inserting a catheter into a blood vessel, directing it to the blood vessels supplying the brain, and suctioning/trapping the clot, which is then withdrawn from the body.

Questions About Interventional Neuroradiology
Question: Who determines if I can or should have an interventional neuroradiology procedure?
Answer: The Radiologist, the patient’s Primary Care Physician and any other physicians involved in your care work as partners. Patients may be referred to St. Paul Radiology by their Primary Care Physician to review your case and/or to review films. Our doctors review and approve, or make other recommendations for procedures. The close relationship between the Radiologist and other physicians promotes the best possible patient care.
Question: How do I schedule an interventional neuroradiology procedure?
Answer: Typically, a nurse from St. Paul Radiology will call you to schedule an appointment once a referral is received from another doctor such as your Primary Care Physician, Neurologist, Neurosurgeon, etc. We have also provided patients and physicians with an easily submitted online form to quickly get the process going directly. The patient may also call 651.917.9930 to schedule an appointment.
Question: Where do these procedures occur?
Answer: Our doctors perform interventional neuroradiology procedures at several hospitals in Minnesota.
Question: How will I get the procedure preparation instructions?
Answer: You will be contacted by a nurse from St. Paul Radiology and be given instructions on how you should prepare for the procedure, as well as where and when to arrive.
Question: What alternatives are available?
Answer: Your Primary Care Physician and a St. Paul Radiology physician will discuss and agree on recommended treatment options for your care.
Question: Who will perform the procedure?
Answer: St. Paul Radiology physicians Jason J. Carroll, M.D., James K. Goddard III, M.D., Jeffrey P. Lassig, M.D., Michael T. Madison, M.D. and Dr. Collin M. Torok, M.D. perform interventional neuroradiology procedures at multiple hospitals in Minnesota. We work with you to make the experience as convenient as possible.

Interventional Neuroradiology Providers at St. Paul Radiology
Our Interventional Neuroradiology group at St. Paul Radiology is uniquely positioned to provide you minimally invasive treatments of brain and spine diseases with the highest quality of care available.

Scheduling Your Interventional Neuroradiology Procedure
Patients do need a referral from their specialist, surgeon or primary care physician for any interventional neuroradiology procedure. We also have a clinic to meet patients and review their imaging and management plans in depth. A St. Paul Radiology nurse will call you to make arrangements with you for your procedure, answer all questions, and notify you of preparation instructions. Remember, if you have imaging studies that were not done at St. Paul Radiology, we ask that you arrange to have the CD's of each study sent to the Interventional Radiology clinic 2-3 days in advance of your scheduled procedure.
Call 651.917.9930 for the minimally invasive experts at St. Paul Radiology.

Advancing Health Through Research
The Physicians on the medical staff at St. Paul Radiology are not only dedicated to improving the health and well-being of their patients but are also committed to advancing the field of Radiology for future generations. Our physicians are actively engaged in professional dialogue that benefits patient care through researching and publishing timely, pertinent, and important topics affecting the practice of Radiology. As a result, they improve their practices and serve as valuable assets to healthcare systems.
Interventional Neuroradiology Publications
- CJ, Patel AP, Walcott BP, Torok CM, Koch MJ, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Rabinov JD, Butler WE, Patel AB. Surgical management of superior petrosal sinus dural arteriovenous fistulae with dominant internal carotid artery supply. Interv Neuroradiol. 2018 Jun;24(3):331-338. doi: 10.1177/1591019917754038. Epub 2018 Feb 12. PubMed PMID: 29433364; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5967184.
- Walcott BP, Stapleton CJ, Torok CM, Patel AB. Flow Diversion for the Treatment of an Unruptured Paraclinoid Carotid Artery Aneurysm. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2017 Aug 1;13(4):537. doi: 10.1093/ons/opw039. PMID: 28838122
- Stapleton CJ, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Torok CM, Hakimelahi R, Hirsch JA, Yoo AJ, Rabinov JD, Patel AB. A direct aspiration first-pass technique vs stentriever thrombectomy in emergent large vessel intracranial occlusions. J Neurosurg. 2017 Apr 14:1-8. doi: 10.3171/2016.11.JNS161563. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 28409731.
- Koch MJ, Stapleton CJ, Agarwalla PK, Torok C, Shin JH, Coumans JV, Borges LF, Ogilvy CS, Rabinov JD, Patel AB. Open and endovascular treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: a 10-year experience. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017 Jan 20:1-5. doi: 10.3171/2016.9.SPINE16394. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 28106525.
- Stapleton CJ, Torok CM, Patel AB. Early experience with the Penumbra SMART coil in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms: Safety and efficacy. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016 Sep 8. pii: 1591019916663479. PMID: 27609753
- Torok CM, Nogueira RG, Yoo AJ, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Hirsch JA, Stapleton CJ, Patel AB, Rabinov JD. Transarterial venous sinus occlusion of dural arteriovenous fistulas using ONYX. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016 Aug 16. pii: 1591019916663478. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 27530138
- Koch M, Stapleton CJ, Agarwalla PK, Torok CM, Shin JH, Coumans JV, Borges LF, Ogilvy CS, Rabinov JD, Patel AB. Open and Endovascular Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae: A 10-Year Experience. Neurosurgery. 2016 Aug;63 Suppl 1:163. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000489726.46488.41. PMID: 27399436
- Stapleton CJ, Torok CM, Patel AB. Noninferiority of a Direct Aspiration First-Pass Technique vs. Stent Retriever Thrombectomy in Emergent Large-Vessel Intracranial Occlusions. Neurosurgery. 2016 Aug; 63 Suppl 1:146-7. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000489681.90969.21. PMID: 27399390.
- Stapleton CJ, Kumar JI, Walcott BP, Torok CM, Agarwalla PK, Koch MJ, Patel AB. The effect of basilar artery bifurcation angle on rates of initial occlusion, recanalization, and retreatment of basilar artery apex aneurysms following coil embolization. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016 Feb 27. pii: 1591019916633243. PMID: 26922975
- Stapleton CJ, Torok CM, Rabinov JD, Walcott BP, Mascitelli JR, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Hirsch JA, Yoo AJ, Ogilvy CS, Patel AB. Validation of the Modified Raymond-Roy classification for intracranial aneurysms treated with coil embolization. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015 Oct 5. pii: neurintsurg-2015-012035. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-012035. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 26438554
- Robert M. Koffie, Christopher J. Stapleton, Collin M. Torok, Albert J. Yoo, Thabele M. Leslie-Mazwi, Patrick J. Codd. Rapid growth of an infectious intracranial aneurysm with catastrophic intracranial hemorrhage. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2014.09.007 [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 25455738
- Pearl MS, Torok C, Katz Z, Messina SA, Blasco J, Tamargo RJ, Huang J, Leigh R, Zeiler S, Radvany M, Ehtiati T, Gailloud P.Pearl MS. Diagnostic quality and accuracy of low dose 3D-DSA protocols in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014 Apr 8. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011137. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 24714612
- Pearl MS, Torok CM. Practical Techniques for Reducing Radiation Exposure During Cerebral Angiography Procedures. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014 Jan 31. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010982. [Epub ahead of print] PMID 24489125.
- Torok CM, Lee C, Nagy P, Yousem DM, Lewin JS. Neuroradiology second opinion consultation service: assessment of duplicative imaging.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013 Nov;201(5):1096-100. doi: 10.2214/AJR.12.9429. PMID 24147482.
- Pearl MS, Torok CM, Messina SA, Radvany M, Rao SN, Ehtiati T, Thompson CB, Gailloud P. Reducing radiation dose while maintaining diagnostic image quality of cerebral three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography: an in vivo study in swine. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013 Oct 11. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010914. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 24122004.
- Torok C, Pearl M. Transvenous coil embolization of an indirect, Barrow type D carotid-cavernous fistula in a 3-year-old with Down syndrome. Journal of Pediatric Neuroradiology. J Pediatr Neuroradiol 2013 Jan;2(2).
- Torok C, Laufer I, Gailloud P. Spontaneous resolution of a thoracic spinal epidural arteriovenous fistula caused by stabbing injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 May 15;38(11):E683-6. PMID: 23429688.
- Li Y, Foss CA, Summerfield DD, Doyle JJ, Torok CM, Dietz HC, Pomper MG, Yu SM.Targeting collagen strands by photo-triggered triple-helix hybridization. ProcNatl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 11;109(37):14767-72. PMID: 22927373.
- Kuo GP, Torok CM, Aygun N, Zinreich SJ. Diagnostic Imaging of the Upper Airway. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011 Mar; 8(1):40-5. PMID 21364220.
- Madison MT, Defillo A, Lassig JP, Zelensky A, Pulivarthi S, Nussbaum ES: Pipeline Embolization for the Treatment of a Progressively Enlarging Symptomatic Carotid Artery Petrous Segment Pseudoaneurysm. Case Report. Cureus 5(7): e131, 2013.
- Nussbaum ES, Graupman P, Goddard JK, Kallmes KM. Air gun orbitocranial penetrating injury: emergency endovascular treatment and surgical bypass following pellet migration to middle cerebral artery: case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2018 Mar;21(3):270-277. doi: 10.3171/2017.8.PEDS17320. Epub 2017 Dec 22. PubMed PMID: 29271732.
- Nussbaum ES, Madison MT, Goddard JK, Lassig JP, Kallmes KM, Nussbaum LA. Microsurgical treatment of unruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysms: a large, contemporary experience. J Neurosurg. 2018 Jun 22:1-7. doi: 10.3171/2018.1.JNS172466. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 29932382.
- Nussbaum ES, Kallmes KM, Lassig JP, Goddard JK, Madison MT, Nussbaum LA: Cerebral Revascularization for the Management of Complex Intracranial Aneurysms: A Single Center Experience. J Neurosurg (accepted for publication)
- Delgado N, Carroll JJ, Meyers PM. Concomitant carotid aplasia and basilar artery occlusion in a child with PHACES syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017. PMID: 28814594
- Carroll JJ, Lavine SD, Meyers PM. Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. In: Levine SR, editor-in-chief. MedLink Neurology. San Diego: MedLink Corporation. Available at
www.medlink.com/article/endovascular_treatment_of_.... - Carroll JJ, Lavine SD, Meyers PM. Imaging of Subdural Hematomas. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2017;28(2):179-203. PMID: 28325453

